In today’s electronic world, devices often require different voltage levels to operate safely and efficiently. A multi voltage power supply provides the flexibility to power various devices without needing multiple adapters. From DIY projects to industrial applications, understanding how to make or select a multi-voltage adapter is essential for convenience, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
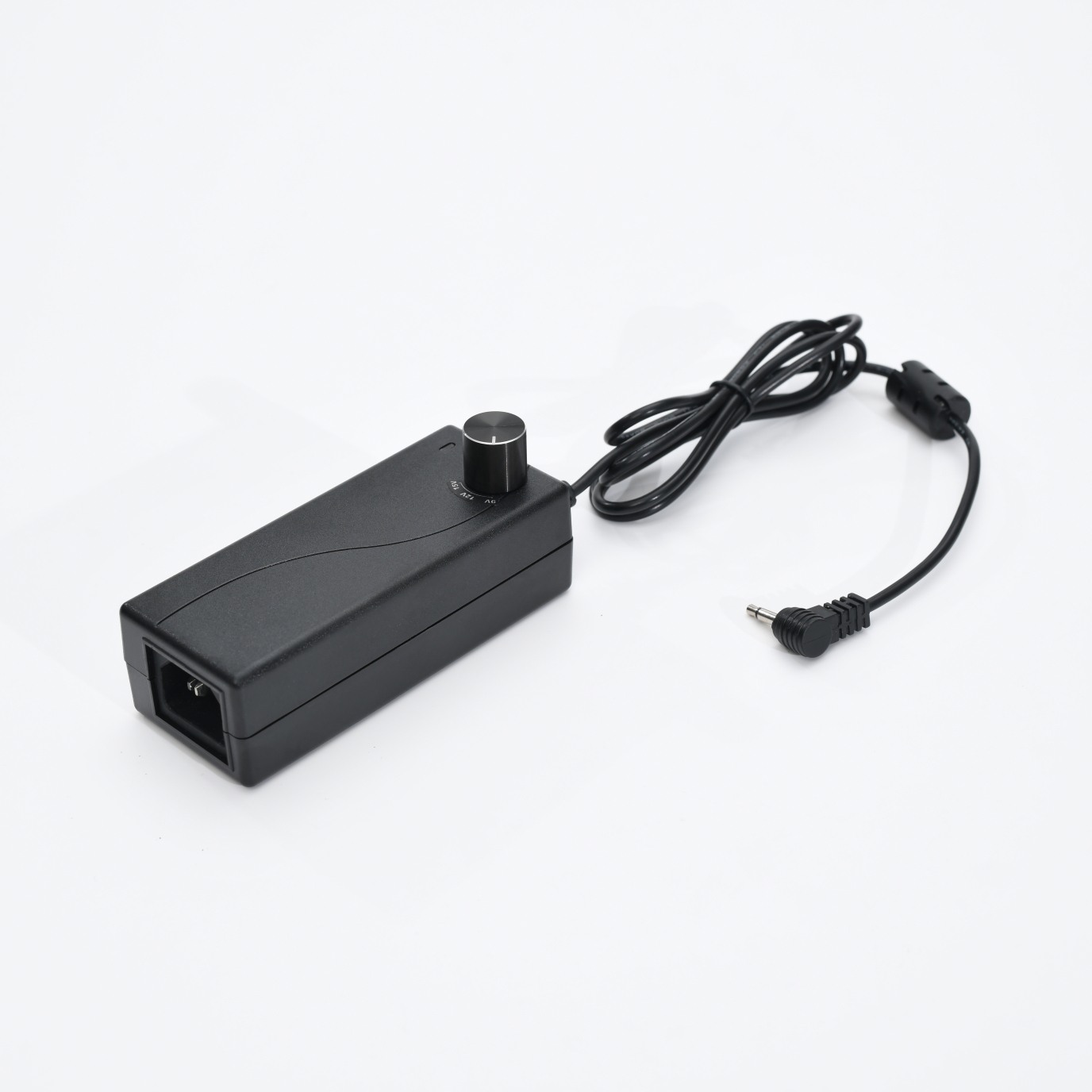

What Is a Multi-Voltage Power Supply?
A multi-voltage power supply is an electronic device capable of providing several output voltage levels from a single input source. Unlike standard adapters that supply only one voltage, multi-voltage solutions allow the user to select the appropriate voltage for different devices, such as routers, LED lights, or electronic instruments.
Some common types include:
Multi voltage AC adapter
Multi voltage DC adapter
Adjustable multi-voltage adapters for DIY electronics
Key Components of a Multi-Voltage Adapter
To build or understand a multi-voltage adapter, it is important to know its main components:
Transformer – Converts the input AC voltage to a desired range. Multi-tap transformers can provide multiple AC voltage outputs.
Rectifier – Converts AC voltage into DC voltage if needed.
Voltage Regulator – Ensures consistent output voltage, even if input voltage fluctuates. Adjustable regulators are common in multi voltage power supplies.
Switching Selector – Allows users to select the required voltage output, commonly found in commercial multi voltage AC adapters.
Protection Circuitry – Includes fuses, over-voltage, and short-circuit protection to safeguard devices.
Steps to Make a Multi-Voltage Power Supply
Determine Voltage Requirements – Identify the range of voltages you need for your devices. Common outputs include 5V, 9V, 12V, 15V, and 24V.
Choose a Transformer or Switching Power Module – For AC applications, a transformer with multiple taps is ideal. For DC devices, a switching power supply with adjustable output is more efficient.
Add Rectifier and Filter Capacitors – If AC-to-DC conversion is required, a bridge rectifier and filter capacitors are essential to produce smooth DC voltage.
Install Voltage Regulators – Use adjustable regulators or fixed regulator ICs to achieve stable output for each voltage.
Wire the Voltage Selector Switch – Connect a switch that allows you to choose the desired voltage output. Ensure correct labeling to prevent damage to connected devices.
Test the Output Voltages – Use a multimeter to check each voltage output under load conditions to ensure stability and safety.
Enclose the Circuit in a Safe Case – Use an insulated case to protect the circuit and the user, especially when handling AC input.
Advantages of a Multi-Voltage AC Adapter
Versatility – One adapter can power multiple devices with different voltage requirements.
Convenience – Eliminates the need for multiple adapters cluttering your workspace.
Cost-Effective – Reduces the need to purchase separate adapters for each device.
Compact Design – Modern multi voltage adapters are small and lightweight, ideal for travel or office use.
Applications of Multi-Voltage Power Supplies
Multi-voltage power supplies are widely used in:
DIY electronics and hobbyist projects
Testing and repairing electronic devices
Industrial machines requiring different voltage inputs
Consumer devices like laptops, routers, and LED lighting
Travel adapters for multiple international devices
Choosing the Right Multi-Voltage Adapter
When selecting a multi voltage adapter, consider:
Supported voltage range
Maximum current rating
Type of output (AC or DC)
Safety certifications (CE, UL, RoHS)
Adjustable vs. fixed voltage options
A multi-voltage power supply or multi-voltage adapter is a practical solution for powering diverse electronic devices safely and efficiently. Whether you are building your own or purchasing a commercial AC adapter multi-voltage solution, understanding the components and proper usage is essential for optimal performance and device protection.